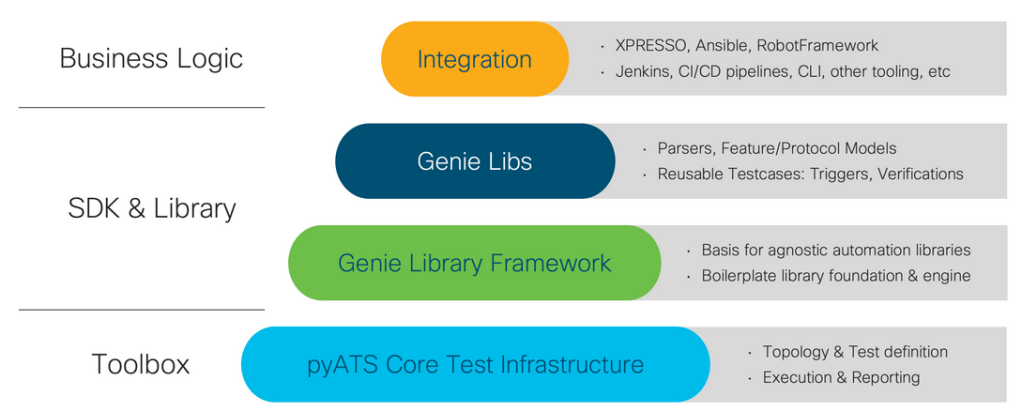
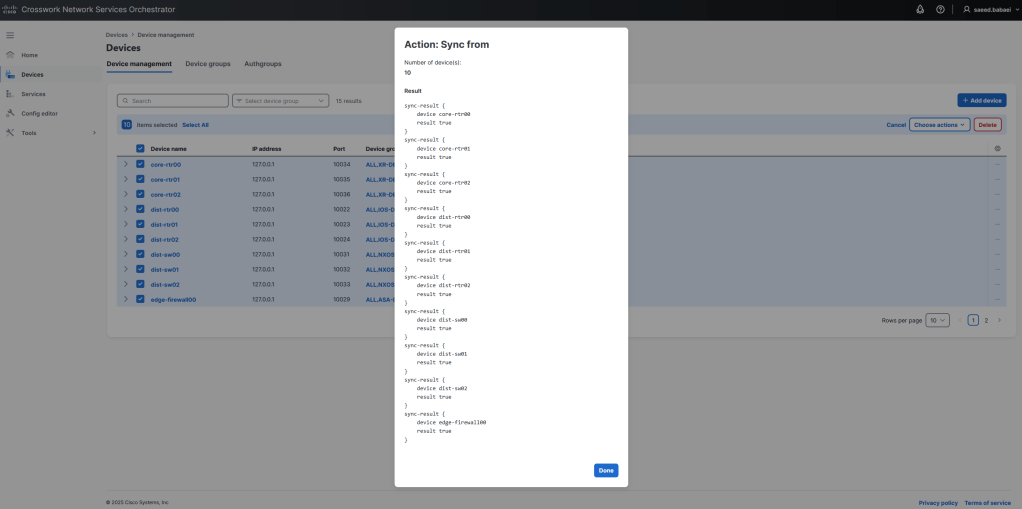
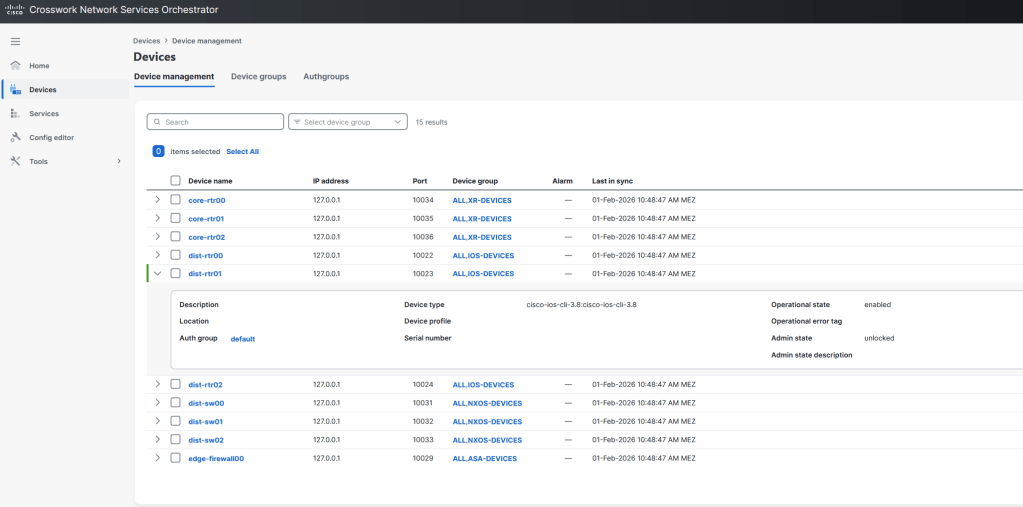
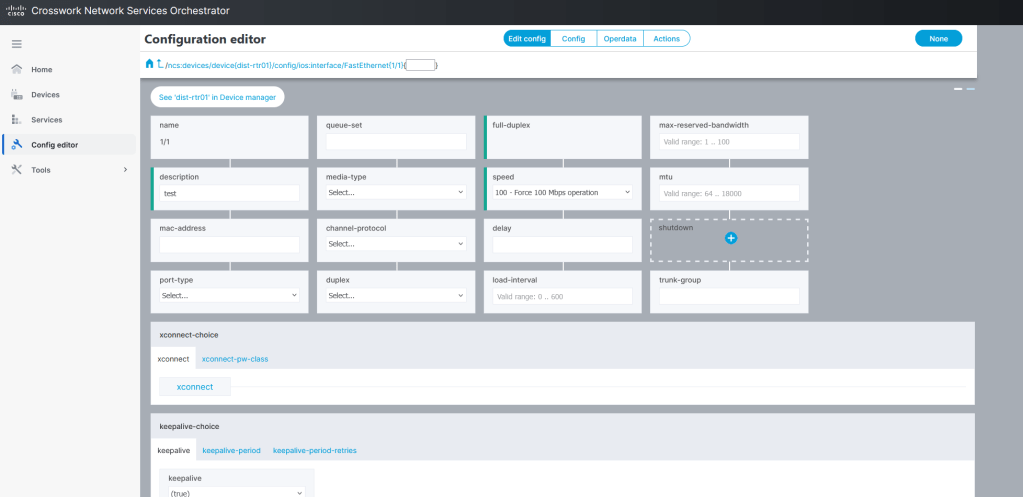
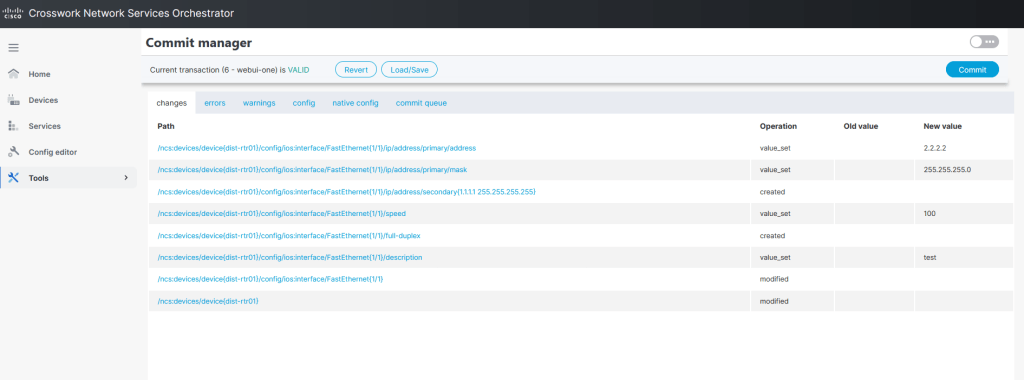
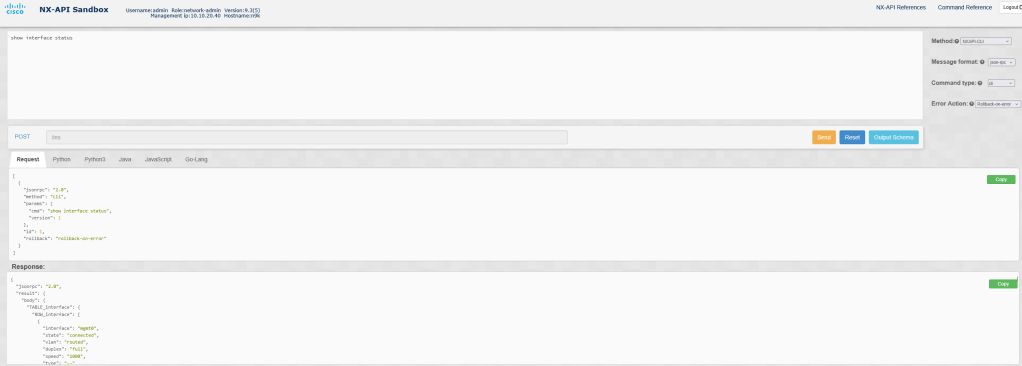
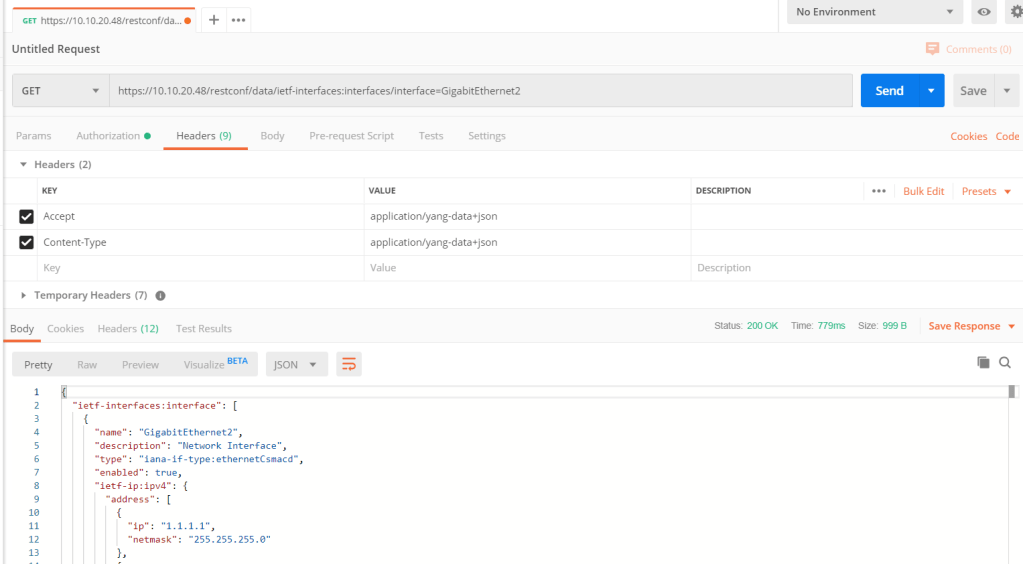
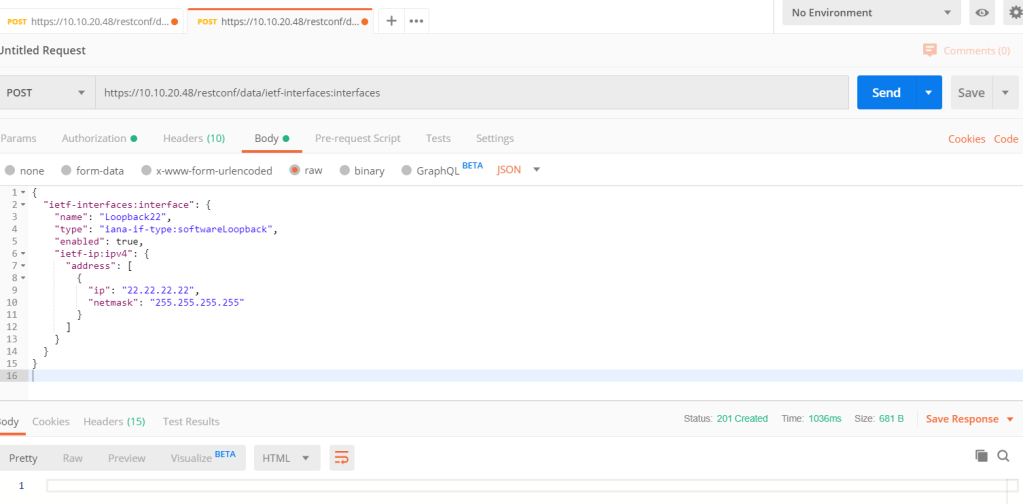
Here is a small but powerful automation tool that:
- Connects to Cisco IOS-XE routers using pyATS
- Parses
show ip interface briefusing Genie - Reduces the structured data
- Sends it to an LLM (OpenAI)
- Receives an AI-based health analysis
- Prints a structured troubleshooting summary
This is a practical example of combining Network Automation + AI-driven operations. In order to use OpenAI API you should have credit there.
Project Structure:
AI/
├── interface_health_check.py
├── testbed.yaml
├── R1_show_ip_int_brief_full.json
├── R1_show_ip_int_brief_compact.json
├── R2_show_ip_int_brief_full.json
├── R2_show_ip_int_brief_compact.json
└── venv/
testbed.yaml:
---
devices:
R1:
os: iosxe
type: iosxe
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 192.168.199.30
credentials:
default:
username: admin
password: cisco
enable:
password: cisco
R2:
os: iosxe
type: iosxe
connections:
cli:
protocol: ssh
ip: 192.168.199.31
credentials:
default:
username: admin
password: cisco
enable:
password: cisco
Workflow Overview:
Connect to device
↓
Run show ip interface brief
↓
Genie parses CLI → structured JSON
↓
Reduce JSON to only relevant fields
↓
Send structured data to OpenAI
↓
Receive troubleshooting summary
↓
Print health analysis
Code:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import os
import json
import logging
from pyats.topology import loader
from openai import OpenAI
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
log = logging.getLogger("pyats-ai")
OPENAI_API_KEY = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
if not OPENAI_API_KEY:
raise RuntimeError("Set OPENAI_API_KEY first (see steps below).")
client = OpenAI(api_key=OPENAI_API_KEY)
TESTBED_FILE = "testbed.yaml"
testbed = loader.load(TESTBED_FILE) #This loads all devices defined in YAML into a Python object
def save_json(data, filename):
with open(filename, "w") as f:
json.dump(data, f, indent=2)
def summarize_int_brief(parsed):
"""
Reduce the parsed output to only what the AI needs.
Genie schema can vary a bit; we defensively extract fields.
"""
rows = []
# Common structure: parsed["interface"] -> dict of interfaces
iface_dict = parsed.get("interface", {})
for ifname, info in iface_dict.items():
rows.append({
"interface": ifname,
"ip_address": info.get("ip_address"),
"status": info.get("status"),
"protocol": info.get("protocol"),
})
# If parser structure differs, fall back to raw object (last resort)
if not rows:
return {"raw": parsed}
return {"interfaces": rows}
#controlled AI reasoning with: Define the AI role+Give clear instructions+Define expected output format+Inject structured JSON
def analyze_with_ai(device_name, payload):
prompt = f"""
You are a Cisco network troubleshooting assistant.
Analyze the following structured output from "show ip interface brief" for device {device_name}.
1) List any interfaces that look unhealthy (down/down, administratively down, protocol down, missing IP where expected).
2) Give likely causes and quick checks/commands.
3) Provide a short "overall health" summary.
Return the answer in clear bullet points.
Data:
{json.dumps(payload, ensure_ascii=False)}
""".strip()
# Responses API (recommended) [Calling the OpenAI API]
resp = client.responses.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
input=prompt,
)
return resp.output_text
for device_name, device in testbed.devices.items():
log.info(f"Connecting to {device_name} ({device.connections.cli.ip}) ...")
try:
device.connect(
log_stdout=False,
init_exec_commands=[],
init_config_commands=[],
)
except Exception as e:
log.error(f"[{device_name}] connect failed: {e}")
continue
try:
log.info(f"[{device_name}] parsing: show ip interface brief")
parsed = device.parse("show ip interface brief")
save_json(parsed, f"{device_name}_show_ip_int_brief_full.json")
compact = summarize_int_brief(parsed)
save_json(compact, f"{device_name}_show_ip_int_brief_compact.json")
log.info(f"[{device_name}] sending to AI...")
ai_text = analyze_with_ai(device_name, compact)
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print(f"AI analysis for {device_name}\n")
print(ai_text)
print("=" * 70 + "\n")
except Exception as e:
log.error(f"[{device_name}] error: {e}")
finally:
device.disconnect()
log.info("Done.")
Output:
(venv) saeed@saeed-ubuntu:~/Desktop/Network-Automation/pyats-lab/AI$ python3 interface_health_check.py
INFO:pyats-ai:Connecting to R1 (192.168.199.30) ...
INFO:pyats-ai:[R1] parsing: show ip interface brief
INFO:pyats-ai:[R1] sending to AI...
INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/responses "HTTP/1.1 429 Too Many Requests"
INFO:openai._base_client:Retrying request to /responses in 0.465011 seconds
INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/responses "HTTP/1.1 429 Too Many Requests"
INFO:openai._base_client:Retrying request to /responses in 0.818862 seconds
INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/responses "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
======================================================================
AI analysis for R1
### Unhealthy Interfaces
- **GigabitEthernet0/1**
- Status: Admin down
- Protocol: Down
- IP Address: Unassigned
- **GigabitEthernet0/2**
- Status: Admin down
- Protocol: Down
- IP Address: Unassigned
- **GigabitEthernet0/3**
- Status: Admin down
- Protocol: Down
- IP Address: Unassigned
### Likely Causes and Quick Checks/Commands
- **GigabitEthernet0/1, 0/2, 0/3**
- **Cause:** These interfaces are administratively down, which typically means they have been shut down via configuration.
- **Quick Check/Commands:**
- Use `show running-config interface GigabitEthernet0/1` (or 2, 3) to verify if the `shutdown` command is applied.
- If they need to be activated, use `interface GigabitEthernet0/1` followed by `no shutdown`.
### Overall Health Summary
- **Overall Health:**
- **GigabitEthernet0/0**: Healthy, active with an assigned IP.
- **Loopback0 & Loopback100**: Healthy, both up but have no assigned IPs, which is acceptable for loopback interfaces.
- **GigabitEthernet0/1, 0/2, & 0/3**: Unhealthy, requiring administrative action to bring them up.
In summary, the main concern is with the administratively down interfaces, which need to be reviewed and possibly activated based on network design requirements.
======================================================================
INFO:pyats-ai:Connecting to R2 (192.168.199.31) ...
INFO:pyats-ai:[R2] parsing: show ip interface brief
INFO:pyats-ai:[R2] sending to AI...
INFO:httpx:HTTP Request: POST https://api.openai.com/v1/responses "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"
======================================================================
AI analysis for R2
### Unhealthy Interfaces
- **GigabitEthernet0/1**
- Status: administratively down
- Protocol: down
- IP Address: unassigned
- **GigabitEthernet0/2**
- Status: administratively down
- Protocol: down
- IP Address: unassigned
- **GigabitEthernet0/3**
- Status: administratively down
- Protocol: down
- IP Address: unassigned
### Likely Causes and Quick Checks
- **GigabitEthernet0/1, 0/2, 0/3 - Administratively Down**
- **Cause**: Interfaces are manually disabled.
- **Quick Check**: Use `show running-config interface GigabitEthernet0/x` to verify the administrative status.
- **Command to Check**: `no shutdown` command in configuration mode to enable the interface if needed.
- **Loopback Interfaces**
- They are up but have unassigned IP addresses, which may not be a problem if not needed for routing or services but should be checked.
- It’s fine if loops are not assigned based on the network design.
### Overall Health Summary
- **Healthy Interfaces**: GigabitEthernet0/0 is operational with an assigned IP.
- **Unhealthy Interfaces**: Three GigabitEthernet interfaces are administratively down, indicating they are disabled intentionally or due to configuration.
- **Action Required**: Review the configuration for the down interfaces and enable as needed based on network requirements. Loopback interfaces require verification to see if IP assignment is actually necessary.
======================================================================
INFO:pyats-ai:Done.
(venv) saeed@saeed-ubuntu:~/Desktop/Network-Automation/pyats-lab/AI$ cat R1_show_ip_int_brief_compact.json
{
"interfaces": [
{
"interface": "GigabitEthernet0/0",
"ip_address": "192.168.199.30",
"status": "up",
"protocol": "up"
},
{
"interface": "GigabitEthernet0/1",
"ip_address": "unassigned",
"status": "administratively down",
"protocol": "down"
},
{
"interface": "GigabitEthernet0/2",
"ip_address": "unassigned",
"status": "administratively down",
"protocol": "down"
},
{
"interface": "GigabitEthernet0/3",
"ip_address": "unassigned",
"status": "administratively down",
"protocol": "down"
},
{
"interface": "Loopback0",
"ip_address": "unassigned",
"status": "up",
"protocol": "up"
},
{
"interface": "Loopback100",
"ip_address": "unassigned",
"status": "up",
"protocol": "up"
}
]
}(venv) saeed@saeed-ubuntu:~/Desktop/Network-Automation/pyats-lab/AI$ cat R1_show_ip_int_brief_full.json
{
"interface": {
"GigabitEthernet0/0": {
"ip_address": "192.168.199.30",
"interface_is_ok": "YES",
"method": "NVRAM",
"status": "up",
"protocol": "up"
},
"GigabitEthernet0/1": {
"ip_address": "unassigned",
"interface_is_ok": "YES",
"method": "NVRAM",
"status": "administratively down",
"protocol": "down"
},
"GigabitEthernet0/2": {
"ip_address": "unassigned",
"interface_is_ok": "YES",
"method": "NVRAM",
"status": "administratively down",
"protocol": "down"
},
"GigabitEthernet0/3": {
"ip_address": "unassigned",
"interface_is_ok": "YES",
"method": "NVRAM",
"status": "administratively down",
"protocol": "down"
},
"Loopback0": {
"ip_address": "unassigned",
"interface_is_ok": "YES",
"method": "unset",
"status": "up",
"protocol": "up"
},
"Loopback100": {
"ip_address": "unassigned",
"interface_is_ok": "YES",
"method": "unset",
"status": "up",
"protocol": "up"
}
}